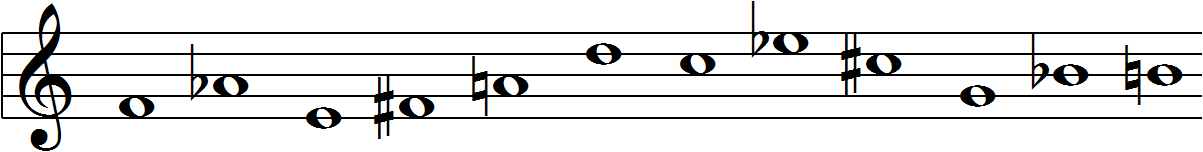
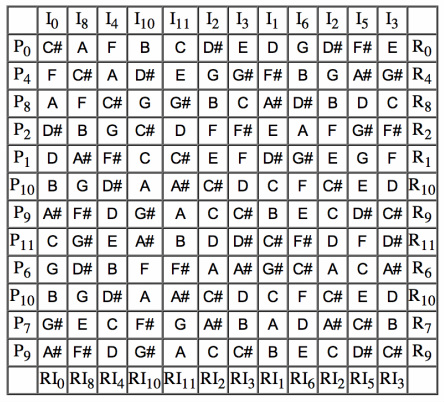
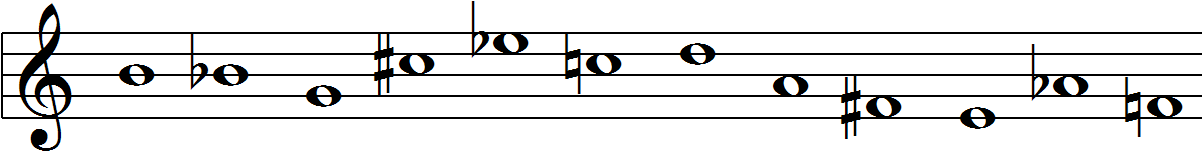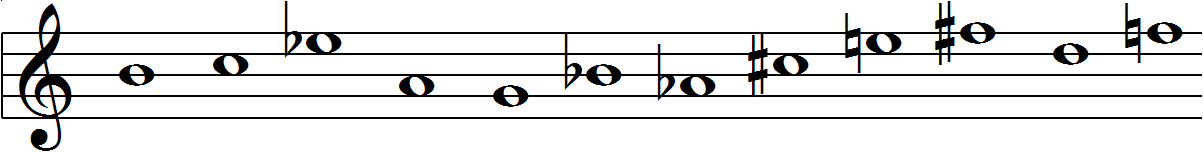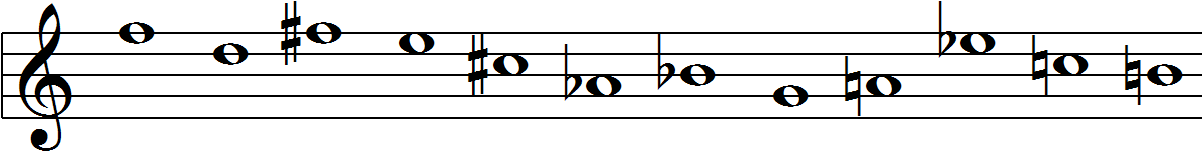Invented by 20th century comopser Arnold Schoenberg, the 12-tone matrix is a compositional tool used by composers to produce 12-tone music. ("Twelve-tone technique") The technique's purpose is to ensure that the consequent music is atonal, meaning that no particular pitch occurs more frequently than another and there is no perceptible key. ("Twelve-tone technique") It serves to emphasize the intervallic relationships created by the composer's matrix rather than relying on the intervallic relationships present in tranditional tonal music. ("Twelve-tone technique") 12-tone music is considered a form of serialization and therefore relies on the very particular ordering of the 12 pitches in the octave. ("Twelve-tone technique") It also relies on the notion of octave equivalence, meaning that the pitches within different octaves are considered equivalent. ("Twelve-tone technique")